Derive an expression to calculate capacitance of spherical capacitor formed by two concentric shell of radii (a) and (b)?
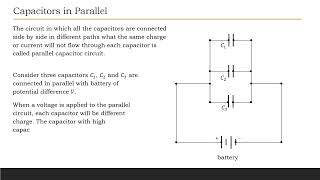
CAPACITANCE OF SPHERICAL CAPACITOR
Consider a spherical capacitor consists of two spherical concentric shells. The inner spherical shell has radius "\(a\)" and charge \(+Q\). The outer spherical shell has radius "\(b\)" and charge \(-Q\) as shown in fig.
The electric field lines are radial and directed outward from inner shell (+ve plate) to outer shell (-ve plate).
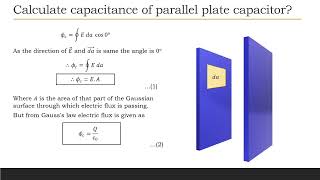
Imagine a Gaussian sphere of radius \(r\) which encloses inner spherical amount of flux diverging out of Gaussian sphere through small area element \(da\) of this Gaussian surface. $$ d\phi_c=\ \vec{E}.\vec{da}\ $$ $$ d\phi_c=\ E.da\ \cos{0}\ $$ $$ d\phi_c=\ E.da\ $$ Net flux through whole Gaussian sphere is $$ \phi_c\ =\oint{E.da} $$ $$ \phi_c=\ E.\left(4\pi r^2\right)\ $$
. . . . . . . . . . . . . (1)
Gauss's law is $$ \phi_c\ =\ \frac{Q}{\varepsilon_0} $$
. . . . . . . . . . . . . (2)
Comparing eq(1) and eq(2) $$ E.\left(4\pi r^2\right)\ =\ \frac{Q}{\varepsilon_0} $$ $$ E\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi r^2\right)\varepsilon_0} $$ It is the magnitude of electric field at any point on the Gaussian sphere due to uniform charge distribution of spherical capacitor.
Potential difference between the shells of the capacitor is $$ V\ =\ \int_{a}^{b}{E\ ds} $$ $$ V\ =\ \int_{a}^{b}{\frac{Q}{\left(4\pi r^2\right)\varepsilon_0}\ dr} $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\int_{a}^{b}{r^{-2}\ dr} $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{r^{-2+1}}{-2+1}\right]_a^b $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{r^{-1}}{-1}\right]_a^b $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{-1}{r}\right]_a^b $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1}{b}\right] $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{b-a}{ab}\right] $$ $$ \frac{Q}{V}=\ \left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0\left[\frac{ab}{b-a}\right] $$
. . . . . . . . . . . . . (3)
The capacitance of spherical capacitor is $$ \frac{Q}{V}=C $$
. . . . . . . . . . . . . (4)
Comparing eq (3) and eq (4) $$ C=\ \left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0\left[\frac{ab}{b-a}\right] $$ This is capacitance of spherical capacitor. It depends upon radius of inner shell and radius of outer spherical shell of capacitor.
ISOLATED SPHERE:
The positively charged inner spherical shell is called isolated sphere negatively charged outer spherical shell is moved at infinity distance. The potential is $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1}{b}\right] $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0}\left[\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1}{\infty}\right] $$ $$ V\ =\ \frac{Q}{\left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0a} $$ $$ \frac{Q}{V}=\ \left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0a $$ $$ C=\ \left(4\pi\right)\varepsilon_0a $$ This is capacitance of isolated sphere.
Write your Comment
Please or to post comment!
No comments yet.
MCQ on Optics (Part 1)
MCQ on Optics (Part 2)
MCQ on Optics (Part 3)
MCQ on Optics (Part 4)
MCQ on Optics (Part 5)
Write a note on Charge.